Pancreas Surgery
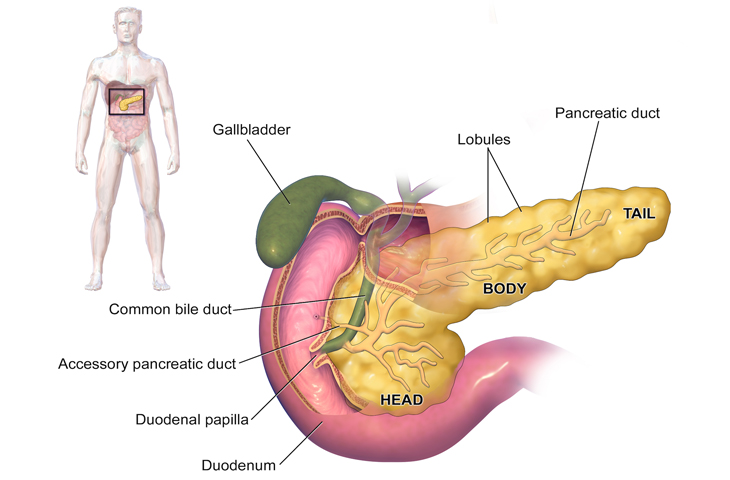
The pancreas is a leaf shaped organ or gland situated deep in the upper abdomen. It is part of the digestive system and produces important enzymes that help break down foods (exocrine function). It also has endocrine function (hormones directly released in blood stream) manly secretion of insulin. It is located in close proximity to stomach, duodenum and bile duct and major blood vessels which make it anatomically difficult to reach organ and make its surgery difficult which involve handling of near by organs also.
Acute pancreatitis:
Acute pancreatitis is sudden inflammation of the pancreas which lead to activation of enzymes that digest food hence can digest pancreas itself. This in turn produces bodies own reaction to this inflammation and affect multiple body systems. Severity of acute pancreatitis can range from mild to life threatening.
Gallstones and alcohol abuse are the main causes of acute pancreatitis.
Severe abdominal pain is the predominant symptom.
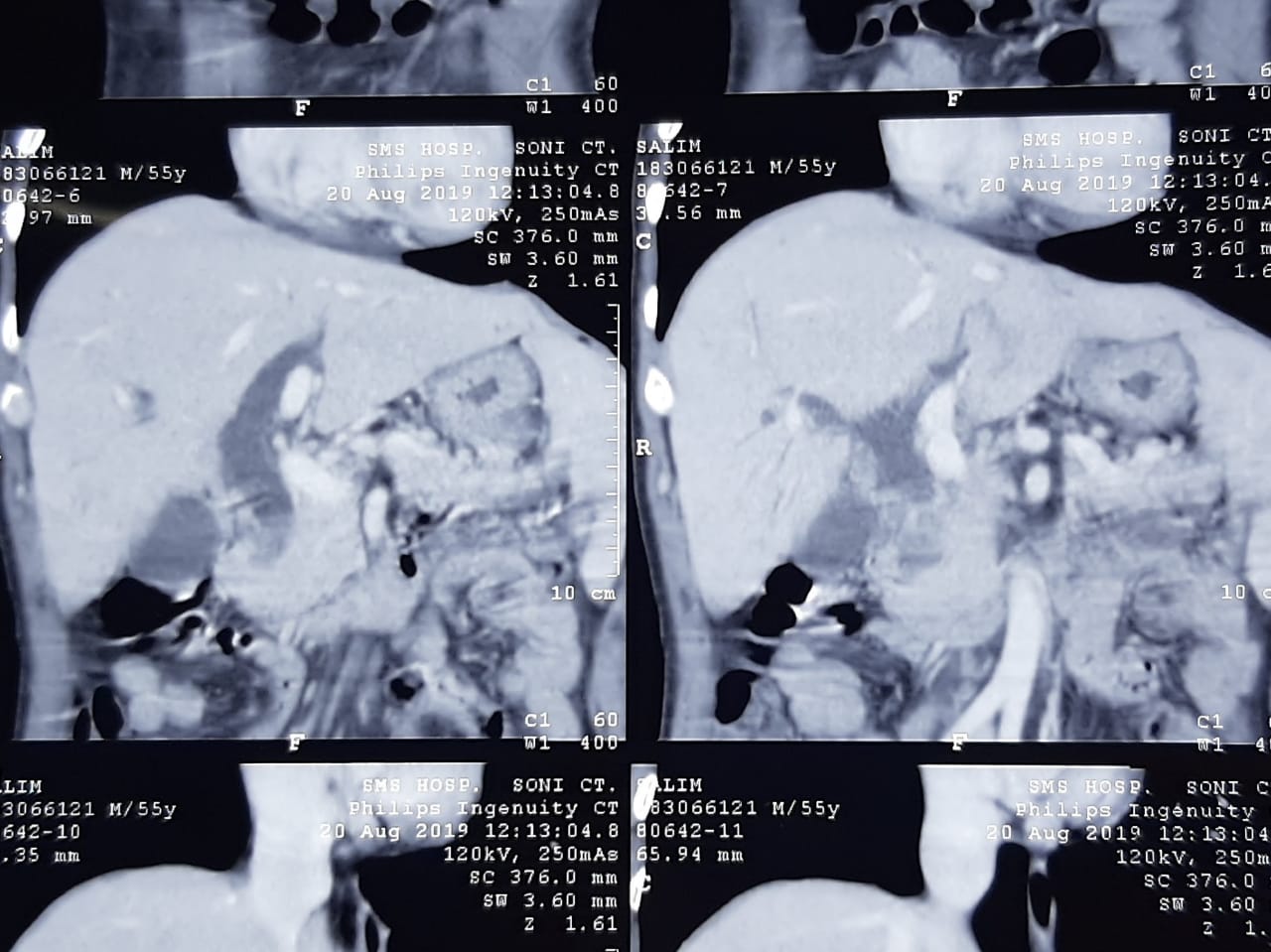
Blood tests such as amylase, lipase levels and imaging tests, such as computed tomography are usually required to make diagnosis.
Whether mild, moderate, or severe, acute pancreatitis usually requires hospitalization.
In early stage it is treated by iv fluids and supporting your body system and in later stages it is treated by controlling the infection by putting one or multiple tubes in body and rarely require a surgery.
Chronic pancreatitis:
Chronic pancreatitis is a long-term progressive inflammatory disease of the pancreas that leads to permanent breakdown of the structure and function of the pancreas. Most commonly affected functions are production of important enzymes and hormones that help break down and digest food and release of insulin to moderate the levels of sugar in the blood.
The most common cause for chronic pancreatitis is long-term alcohol abuse – it is thought to account for approx. 70 percent of all cases.
It presents as long-standing pain in upper abdomen which also radiates to back.
In early stage pain is only symptom and pancreas looks mild atrophic on imaging. It usually diagnosed when stones are seen in pancreatic duct on imaging.
Surgery (frey’s procedure) is procedure of choice for treatment when pain is not relived by pain killer medications.
Pancreatic Cyst
Pancreatic cysts are collections (pools) of fluid that can form within the head, body, and tail of the pancreas. Some pancreatic cysts are true cysts (non-inflammatory cysts), that is, they are lined by a special layer of cells that are responsible for secreting fluid into the cysts. Other cysts are pseudocysts (inflammatory cysts) and do not contain specialized lining cells. Often these pseudocysts contain pancreatic digestive juices because they are connected to the pancreatic ducts. Pancreatic cysts can range in size from several millimeters to several centimeters. Many pancreatic cysts are small and benign and produce no symptoms, but some cysts become large and cause symptoms, and others are cancerous or precancerous.
Pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer is cancer that forms in the cells of the pancreas. Pancreas cancer can be of 2 types cancer of exocrine cells (occurs 90% of total) or cancer of endocrine cells (10% of total). Pancreatic cancer is deadly disease. Its fourth most common cause death world as it usually diagnosed at late stage because its asymptomatic at earlier stages.
Symptoms may include abdominal pain, jaundice and weight loss.
It is usually diagnosed while evaluating a patient for pain abdomen or jaundice. Ca19-9 level may be helpful for diagnosis but has their own limitation.
Multidetector thin slice CT scan is helpful both in diagnosis, staging of disease and in treatment planning.
Surgery is only curative treatment and requires multiorgan resection and complex reconstruction.